Lorentz Force
Lorentz Force: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Magnetic Force, Lorentz Force, Force on a Moving Charge in Magnetic Field, Fleming's Left Hand Rule for the Direction of Magnetic Force, Right Hand Rule for the Direction of Magnetic Force, etc.
Important Questions on Lorentz Force
A particle having charge of , mass and speed enters a uniform magnetic field, having magnetic induction of , at an angle between velocity vector and magnetic induction. The pitch of its helical path is (in meters)
An electron is moving along a positive axis. A uniform electric field exists towards negative axis. What should be the direction of a magnetic field of suitable magnitude, so that the net force of electron is zero.
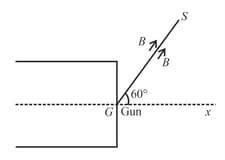
An electron gun G emits electron of energy travelling in the (+)ve x-direction. The electrons are required to hit the spot S where & the line GS makes an angle of with the x-axis, as shown in the fig. A uniform magnetic field parallel to GS exists in the region outsides to electron gun. Find the minimum value of B needed to make the electron hit S.
A circular coil, of radius , carries a current . The expression for the magnetic field due to this coil at its centre is
A beam of proton projected along -axis, experiences a force due to a magnetic field along the -axis. The direction of the magnetic field is:
An electron is moving along +ve x-axis in the presence of uniform magnetic field along +ve y-axis. What is the direction of the force acting on it?
A proton of mass and charge is moving in a circular orbit in a magnetic field with energy . What should be the energy of ( and ), so that it can revolve in the path of same radius.
When a charged particle moves in a straight line a magnetic field is?
How is a charged particle getting deflected in a magnetic field?
What is deviation in magnetic field?
The electron in the beam of a television tube move horizontally from south to north. The vertical component of the earth's magnetic field points down. The electron is deflected towards,
How is the aurora borealis created physics?
What causes northern light aurora borealis?
What happens to a charged particle in a magnetic field?
What causes northern lights' aurora borealis?
A moving electron enters normally into a uniform magnetic field; its:
Why the time period of a charged particle undergoing a circular motion in a uniform magnetic field is independent of its speed.
Pitch of the helical path described by the particle is:
An electron with a mass and charge of , projected into a uniform magnetic field of at a speed of in such a way its velocity makes an angle of with the field lines. Find the period, pitch, and radius of the helical path of the electron.
In the cyclotron,as radius of the circular path of the charged particle increases(=angular velocity, =linear velocity).
